How to Set Realistic Parameters for Forex Testing
Testing Forex strategies is essential for traders aiming to succeed in currency trading. However, without realistic parameters for Forex testing, your results can lead to costly misconceptions.
Understanding how to set these parameters will help you test strategies effectively. Of course, it’s also to achieve more reliable outcomes. Let’s explore how intermediate traders can fine-tune their approach to Forex testing with simple examples and practical tips.
Why Realistic Parameters for Forex Testing Matter
Testing a trading strategy in Forex without proper boundaries can give misleading results. Unrealistic parameters, such as exaggerated win rates or fixed market conditions, won’t reflect real-world trading.
This is where setting achievable goals and testing conditions come into play. By aligning your parameters with actual market behavior, you can evaluate strategies more accurately.
Key Factors to Consider in Parameters for Forex Testing
When setting parameters for Forex testing, consider the following:
1. Market Conditions
The Forex market doesn’t stay constant. Hence, your testing must account for varied conditions such as trends, ranges, and volatility spikes. For example:
- Trending Market: Test strategies with a clear upward or downward trend.
- Ranging Market: Include periods with sideways price movement.
By simulating different conditions, you’ll ensure your strategy performs reliably across diverse scenarios.
2. Timeframes and Data Samples
Using multiple timeframes improves testing accuracy. A daily timeframe might work for swing traders, while a one-hour chart suits scalpers.
Furthermore, test over a wide data range, including at least 5-10 years of historical data, to include various economic cycles.
How to Set Realistic Parameters for Forex Testing
1. Define Entry and Exit Rules
Clear rules for entering and exiting trades are crucial. For instance, a simple moving average (SMA) crossover can form the basis of your entry rule:
- Entry Rule Example: Buy when the 50-SMA crosses above the 200-SMA.
- Exit Rule Example: Sell when the price falls below the 50-SMA.
Test these rules across different market conditions. Adjust parameters to avoid overfitting, which happens when a strategy works only in a specific dataset but fails elsewhere.
2. Set Risk-Reward Ratios
Risk management is central to effective Forex trading. Use ratios like 1:2 (risking $100 to gain $200) for better long-term results.
Example Calculation:
If your average loss is $50 and your average gain is $100, a 1:2 risk-reward ratio keeps you profitable even with a 50% win rate. Ensure this ratio aligns with your trading style and risk tolerance.
3. Account for Slippage and Spread
Ignoring trading costs such as slippage and spreads skews your results. Add these costs to every trade in your test. For example:
- Spread: If the EUR/USD spread is 1 pip and you make 20 trades, include a 20-pip cost.
- Slippage: If slippage averages 0.5 pips per trade, factor in an additional 10 pips over those 20 trades.
By incorporating these, your results reflect real-world profitability.
4. Simulate Position Sizing
Position sizing affects your trading performance and risk. Use the 1-2% rule, risking no more than 1-2% of your account per trade.
Example Calculation:
If your account balance is $10,000 and you risk 2% per trade, your maximum risk is $200. With a stop loss set at 20 pips, your lot size would be:
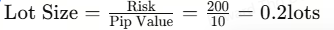
Adjust this for different account sizes and risk preferences.
Optimising Parameters for Forex Testing
1. Backtesting with Automated Tools
Tools like MetaTrader’s Strategy Tester or third-party platforms streamline backtesting. However, avoid over-optimisation, where the strategy becomes too tailored to past data. Use out-of-sample testing to validate your results further.
2. Forward Testing on Demo Accounts
After backtesting, forward-test your strategy in a demo account. This step ensures the strategy works under live market conditions. Monitor your strategy over several months to spot inconsistencies.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid:
- Unrealistic Expectations in Parameters for Forex Testing
Expecting 90% win rates isn’t feasible. Instead, aim for consistency with moderate returns.
2. Ignoring Psychological Factors
Demo testing doesn’t include the emotional pressures of live trading. Transition to a small live account after demo testing to evaluate your readiness.
3. Overlooking Drawdowns
Consider drawdown periods while testing. For instance, if a strategy has a maximum drawdown of 20%, ensure you have enough capital to withstand this.
Conclusion
Setting realistic parameters for Forex testing lays the foundation for a robust trading strategy. By considering market conditions, timeframes, risk-reward ratios, and real-world costs, you’ll develop strategies that stand the test of time.
Use backtesting and forward testing together for comprehensive evaluation, and avoid common pitfalls like over-optimisation and unrealistic expectations.
Start refining your parameters today, and watch your trading strategies reach new levels of effectiveness!
