Basics of Currency Correlations
Currency correlations are an essential concept for anyone venturing into forex trading. They explain the relationship between currency pairs and how they move in relation to one another.
Understanding these correlations can help traders make better-informed decisions, manage risk effectively, and maximise opportunities in the volatile forex market.
In this guide, we’ll break down the basics of currency correlations, explain how they work, and provide simple examples and calculations to help you get started.
What are Currency Correlations?
Currency correlations measure how two currency pairs move relative to each other. A correlation can be positive, negative, or near zero.
- Positive correlation: When two currency pairs move in the same direction. For example, EUR/USD and GBP/USD often rise and fall together.
- Negative correlation: When two currency pairs move in opposite directions. For instance, USD/JPY and EUR/USD typically show this relationship.
- Neutral correlation: When there is little to no relationship between the movements of two pairs.
Correlations are measured using a correlation coefficient ranging from +1 to -1.
A value of +1 means the pairs move perfectly in the same direction. Meanwhile, -1 indicates they move in completely opposite directions. A value close to 0 suggests no strong relationship.
Why Do Currency Correlations Matter in Forex Trading?
For traders, understanding currency correlations is vital for effective risk management and portfolio diversification. Here’s why:
- Risk management: Trading highly correlated pairs simultaneously can increase exposure. For example, going long on EUR/USD and GBP/USD can double your risk if both pairs decline.
- Diversification: Trading pairs with low or negative correlations can help balance your portfolio.
- Better strategies: Knowing correlations can help traders anticipate price movements, especially during market events.
Simple Example of Currency Correlations
Let’s explore a straightforward scenario:
- Currency pair A: EUR/USD
- Currency pair B: GBP/USD
Assume the EUR/USD moves 100 pips up, and GBP/USD also rises by 95 pips. This indicates a strong positive correlation.
To calculate the correlation coefficient, you’d use historical price data. Here’s a basic formula:
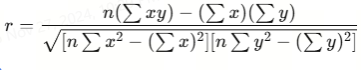
Where:
- xx and yy are the price changes of the two currency pairs.
- nn is the number of data points.
Although this calculation is often handled by trading platforms or tools, understanding the principle helps you appreciate the data driving your trades.
Commonly Correlated Currency Pairs
Certain currency pairs tend to have consistent correlations due to economic ties or trade relationships. Below are a few examples:
Positive correlations
- EUR/USD and GBP/USD: Both are influenced by the USD’s strength or weakness and economic data from Europe and the UK.
- AUD/USD and NZD/USD: Both depend on commodity exports and economic data from their respective regions.
Negative correlations
- USD/JPY and EUR/USD: When the USD strengthens, EUR/USD often falls, and USD/JPY rises.
- USD/CHF and GBP/USD: These pairs frequently move in opposite directions due to the Swiss franc’s safe-haven status.
How to Apply Currency Correlations in your Strategy
Now that you understand the basics, let’s look at how you can use this knowledge in practical trading scenarios:
1. Avoid overexposure
If you’re trading positively correlated pairs like EUR/USD and GBP/USD, remember that a loss in one pair can lead to losses in the other. Consider diversifying by including negatively correlated pairs in your strategy.
2. Use correlations to confirm trades
Correlations can validate your analysis. For instance, if EUR/USD is rising, and GBP/USD shows a similar trend, it may strengthen your confidence in taking a long position.
3. Monitor changing correlations
Currency correlations are not static. Economic events, geopolitical developments, and central bank policies can change correlations. Regularly check updated correlation tables or tools to stay informed.
Practical Examples
Suppose you’re tracking EUR/USD and USD/JPY:
- On Monday, EUR/USD gains 80 pips, while USD/JPY loses 75 pips.
- On Tuesday, EUR/USD gains 50 pips, and USD/JPY loses 45 pips.
Over two days, the correlation appears negative. You can use these insights to anticipate price movements. If EUR/USD continues to rise, you might predict USD/JPY will decline.
Tools to Measure Currency Correlations
Many forex brokers and platforms offer correlation tables to help traders. These tools display the correlation coefficient between currency pairs over specific timeframes, such as one day, one week, or one month.
Look for pairs with strong positive or negative correlations to refine your strategy.
Final thoughts
Understanding the basics of currency correlations can elevate your forex trading skills. It’s a powerful tool for managing risk, diversifying your portfolio, and making more informed decisions.
Start by observing correlations in your preferred currency pairs. Use the insights to improve your trading strategy. Over time, you’ll notice how this knowledge enhances your confidence and results in the forex market.
Happy trading!
